Page 74 - Igor Ž. Žagar in Ana Mlekuž, ur. ▪︎ Raziskovanje v vzgoji in izobraževanju. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut, 2019. Digitalna knjižnica, Dissertationes 37
P. 74
r aziskovanje v vzgoji in izobr aževanju
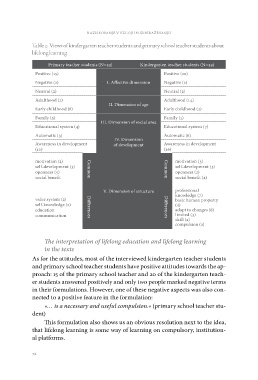
Table 2: Views of kindergarten teacher students and primary school teacher students about
lifelong learning
Primary teacher students (N=22) Kindergarten teacher students (N=29)
Positive (15) Positive (20)
Negative (2) I. Affective dimension Negative (2)
Neutral (2) Neutral (2)
Adulthood (2) II. Dimension of age Adulthood (14)
Early childhood (8) Early childhood (2)
Family (3) III. Dimension of social area Family (1)
Educational system (4) Educational system (7)
Automatic (3) IV. Dimension Automatic (6)
Awareness in development of development Awareness in development
(10) (16)
motivation (2) Common Common motivation (3)
self-development (3) self-development (3)
openness (5) openness (2)
social benefit social benefit (2)
V. Dimension of structure professional
knowledge (7)
value system (2) Differences Differences basic human property
self-knowledge (2) (5)
education adapt to changes (6)
communication limited (3)
skill (2)
compulsion (2)
The interpretation of lifelong education and lifelong learning
in the texts
As for the attitudes, most of the interviewed kindergarten teacher students
and primary school teacher students have positive attitudes towards the ap-
proach: 15 of the primary school teacher and 20 of the kindergarten teach-
er students answered positively and only two people marked negative terms
in their formulations. However, one of these negative aspects was also con-
nected to a positive feature in the formulation:
»… is a necessary and useful compulsion.« (primary school teacher stu-
dent)
This formulation also shows us an obvious resolution next to the idea,
that lifelong learning is some way of learning on compulsory, institution-
al platforms.
74
Table 2: Views of kindergarten teacher students and primary school teacher students about
lifelong learning
Primary teacher students (N=22) Kindergarten teacher students (N=29)
Positive (15) Positive (20)
Negative (2) I. Affective dimension Negative (2)
Neutral (2) Neutral (2)
Adulthood (2) II. Dimension of age Adulthood (14)
Early childhood (8) Early childhood (2)
Family (3) III. Dimension of social area Family (1)
Educational system (4) Educational system (7)
Automatic (3) IV. Dimension Automatic (6)
Awareness in development of development Awareness in development
(10) (16)
motivation (2) Common Common motivation (3)
self-development (3) self-development (3)
openness (5) openness (2)
social benefit social benefit (2)
V. Dimension of structure professional
knowledge (7)
value system (2) Differences Differences basic human property
self-knowledge (2) (5)
education adapt to changes (6)
communication limited (3)
skill (2)
compulsion (2)
The interpretation of lifelong education and lifelong learning
in the texts
As for the attitudes, most of the interviewed kindergarten teacher students
and primary school teacher students have positive attitudes towards the ap-
proach: 15 of the primary school teacher and 20 of the kindergarten teach-
er students answered positively and only two people marked negative terms
in their formulations. However, one of these negative aspects was also con-
nected to a positive feature in the formulation:
»… is a necessary and useful compulsion.« (primary school teacher stu-
dent)
This formulation also shows us an obvious resolution next to the idea,
that lifelong learning is some way of learning on compulsory, institution-
al platforms.
74