Page 69 - Štremfel, Urška, and Maša Vidmar (eds.). 2018. Early School Leaving: Contemporary European Perspectives. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut.
P. 69
the esl situation in france
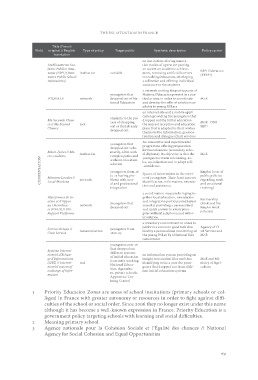
Field Title (French Type of policy Target public Synthetic description Policy carrier
original // English
translation
Etablissements Sco- institution variable an institution offering innova- ESPI federation
laires Publics Inno- tive modes of operation putting (FESPI)
vants (ESPI) (Inno- youngsters that an accent on academic achieve- MoE
vative Public School dropped out of Na- ment, removing artificial barriers MoE - ONI-
Institutions) tional Education in teaching/education, developing SEP15
students in the pro- a collective and offering individual
FOQUALE network cess of dropping assistance to the students MoE
out or that already a network uniting the participants of Emploi (a set of
Ma Seconde Chan- tool dropped out National Education present in a par- public policies
ce // My Second youngsters that ticular area in order to coordinate regarding work
Chance dropped out volu- and develop the offer of solutions av- and vocational
ntarily, often with ailable to young ESLers training)
Micro-lycées // Mi- institution complex paths and an internet site and a mobile appli- Partnership
cro-students without education cation providing the youngsters that (MoE and the
COMPENSATION solution dropped out the initial education Emploi work
Missions Locales // network youngsters from 16 the nearest reception and education policies)
Local Missions to 25 having pro- place that is adapted to their wishes Agency of Ci-
blems with soci- thanks to the information, geoloca- vil Service and
Plateformes de So- network al and professional lisation and dialogue (chat) services MoE
utien et d'Appui integration An innovative and experimental MoE and Mi-
au Décrocheu- youngsters that programme offering preparation nistry of Agri-
rs (PSAD) // ESL dropped out for baccalaureate (secondary scho- culture
Support Platforms ol diploma). Its objective is that the
youngsters from youngsters return to learning, ru-
Service civique // measure/action 16 to 25 les, socialisation and to adopt self-
Civic Service youngsters over 16 -confidence.
that dropped out Spaces of intervention in the servi-
Système Intermi- tool different systems ce of youngsters. Their functions are
nistriel d'Echan- of initial education identification, information, orienta-
ge d'Informations (currently tracking: tion and assistance.
(SIEI) // Intermi- National Educa- a coordination measure bringing to-
nistrial system of tion, Agricultu- gether local education, orientation
exchange of infor- re, private schools, and integration participants/players
mation Apprentice Tra- aimed at providing a personalised
ining Centre) and quick answer to every youn-
gster without a diploma and witho-
ut solution
a voluntary commitment in order to
perform a common good task dou-
bled by a personalised monitoring of
the young ESLer by a National Edu-
cation tutor
an information system providing an
insight into student files and thus
identifying twice a year the youn-
gsters that dropped out from diffe-
rent initial education systems
1 Priority Education Zones are areas of school institutions (primary schools or col-
lèges) in France with greater autonomy or resources in order to fight against diffi-
culties of the school or social order. Since 2006 they no longer exist under this name
although it has become a well-known expression in France. Priority Education is a
government policy targeting schools with learning and social difficulties.
2 Meaning primary school
3 Agence nationale pour la Cohésion Sociale et l’Égalité des chances // National
Agency for Social Cohesion and Equal Opportunities
69
Field Title (French Type of policy Target public Synthetic description Policy carrier
original // English
translation
Etablissements Sco- institution variable an institution offering innova- ESPI federation
laires Publics Inno- tive modes of operation putting (FESPI)
vants (ESPI) (Inno- youngsters that an accent on academic achieve- MoE
vative Public School dropped out of Na- ment, removing artificial barriers MoE - ONI-
Institutions) tional Education in teaching/education, developing SEP15
students in the pro- a collective and offering individual
FOQUALE network cess of dropping assistance to the students MoE
out or that already a network uniting the participants of Emploi (a set of
Ma Seconde Chan- tool dropped out National Education present in a par- public policies
ce // My Second youngsters that ticular area in order to coordinate regarding work
Chance dropped out volu- and develop the offer of solutions av- and vocational
ntarily, often with ailable to young ESLers training)
Micro-lycées // Mi- institution complex paths and an internet site and a mobile appli- Partnership
cro-students without education cation providing the youngsters that (MoE and the
COMPENSATION solution dropped out the initial education Emploi work
Missions Locales // network youngsters from 16 the nearest reception and education policies)
Local Missions to 25 having pro- place that is adapted to their wishes Agency of Ci-
blems with soci- thanks to the information, geoloca- vil Service and
Plateformes de So- network al and professional lisation and dialogue (chat) services MoE
utien et d'Appui integration An innovative and experimental MoE and Mi-
au Décrocheu- youngsters that programme offering preparation nistry of Agri-
rs (PSAD) // ESL dropped out for baccalaureate (secondary scho- culture
Support Platforms ol diploma). Its objective is that the
youngsters from youngsters return to learning, ru-
Service civique // measure/action 16 to 25 les, socialisation and to adopt self-
Civic Service youngsters over 16 -confidence.
that dropped out Spaces of intervention in the servi-
Système Intermi- tool different systems ce of youngsters. Their functions are
nistriel d'Echan- of initial education identification, information, orienta-
ge d'Informations (currently tracking: tion and assistance.
(SIEI) // Intermi- National Educa- a coordination measure bringing to-
nistrial system of tion, Agricultu- gether local education, orientation
exchange of infor- re, private schools, and integration participants/players
mation Apprentice Tra- aimed at providing a personalised
ining Centre) and quick answer to every youn-
gster without a diploma and witho-
ut solution
a voluntary commitment in order to
perform a common good task dou-
bled by a personalised monitoring of
the young ESLer by a National Edu-
cation tutor
an information system providing an
insight into student files and thus
identifying twice a year the youn-
gsters that dropped out from diffe-
rent initial education systems
1 Priority Education Zones are areas of school institutions (primary schools or col-
lèges) in France with greater autonomy or resources in order to fight against diffi-
culties of the school or social order. Since 2006 they no longer exist under this name
although it has become a well-known expression in France. Priority Education is a
government policy targeting schools with learning and social difficulties.
2 Meaning primary school
3 Agence nationale pour la Cohésion Sociale et l’Égalité des chances // National
Agency for Social Cohesion and Equal Opportunities
69