Page 52 - Igor Ž. Žagar in Ana Mlekuž, ur. ▪︎ Raziskovanje v vzgoji in izobraževanju. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut, 2019. Digitalna knjižnica, Dissertationes 37
P. 52
r aziskovanje v vzgoji in izobr aževanju
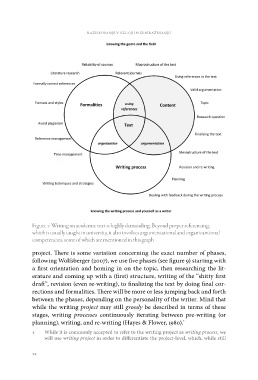
Figure 1: Writing an academic text is highly demanding. Beyond proper referencing,
which is usually taught in university, it also involves argumentational and organizantional
competencies, some of which are mentioned in this graph
project. There is some variation concerning the exact number of phases,
following Wolfsberger (2007), we use five phases (see figure 9) starting with
a first orientation and homing in on the topic, then researching the lit-
erature and coming up with a (first) structure, writing of the “shitty first
draft”, revision (even re-writing), to finalizing the text by doing final cor-
rections and formalities. There will be more or less jumping back and forth
between the phases, depending on the personality of the writer. Mind that
while the writing project may still grossly be described in terms of these
stages, writing processes continuously iterating between pre-writing (or
planning), writing, and re-writing (Hayes & Flower, 1980).1
1 While it is commonly accepted to refer to the writing project as writing process, we
will use writing project in order to differentiate the project-level, which, while still
52
Figure 1: Writing an academic text is highly demanding. Beyond proper referencing,
which is usually taught in university, it also involves argumentational and organizantional
competencies, some of which are mentioned in this graph
project. There is some variation concerning the exact number of phases,
following Wolfsberger (2007), we use five phases (see figure 9) starting with
a first orientation and homing in on the topic, then researching the lit-
erature and coming up with a (first) structure, writing of the “shitty first
draft”, revision (even re-writing), to finalizing the text by doing final cor-
rections and formalities. There will be more or less jumping back and forth
between the phases, depending on the personality of the writer. Mind that
while the writing project may still grossly be described in terms of these
stages, writing processes continuously iterating between pre-writing (or
planning), writing, and re-writing (Hayes & Flower, 1980).1
1 While it is commonly accepted to refer to the writing project as writing process, we
will use writing project in order to differentiate the project-level, which, while still
52