Page 172 - Ana Mlekuž in Igor Ž. Žagar, ur. • Raziskovanje v vzgoji in izobraževanju: Izobraževanje učiteljic in učiteljev za raziskovalno učenje in poučevanje. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut, 2024. Digitalna knjižnica, Dissertationes 48
P. 172
raziskovanje v vzgoji in izobraževanju: izobraževanje učiteljic in učiteljev ...
COVID -19 COVID-19 COVID-19 COVID-19
anxiety anxiety anxiety anxiety
T1 T2 T3 T4
Intercept Slope
-.11 ᵃ
.28**
.05
-.62**
-.02
Emotional Practising
self-efficacy mindfulness
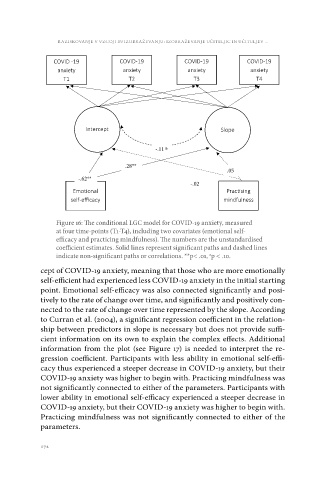
Figure 16: The conditional LGC model for COVID-19 anxiety, measured
at four time-points (T1-T4), including two covariates (emotional self-
efficacy and practicing mindfulness). The numbers are the unstandardised
coefficient estimates. Solid lines represent significant paths and dashed lines
indicate non-significant paths or correlations. **p< .01, p < .10.
a
cept of COVID-19 anxiety, meaning that those who are more emotionally
self-efficient had experienced less COVID-19 anxiety in the initial starting
point. Emotional self-efficacy was also connected significantly and posi-
tively to the rate of change over time, and significantly and positively con-
nected to the rate of change over time represented by the slope. According
to Curran et al. (2004), a significant regression coefficient in the relation-
ship between predictors in slope is necessary but does not provide suffi-
cient information on its own to explain the complex effects. Additional
information from the plot (see Figure 17) is needed to interpret the re-
gression coefficient. Participants with less ability in emotional self-effi-
cacy thus experienced a steeper decrease in COVID-19 anxiety, but their
COVID-19 anxiety was higher to begin with. Practicing mindfulness was
not significantly connected to either of the parameters. Participants with
lower ability in emotional self-efficacy experienced a steeper decrease in
COVID-19 anxiety, but their COVID-19 anxiety was higher to begin with.
Practicing mindfulness was not significantly connected to either of the
parameters.
172