Page 92 - Štremfel, Urška, and Maša Vidmar (eds.). 2018. Early School Leaving: Contemporary European Perspectives. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut.
P. 92
ear ly school leaving: contempor ary european perspectives
typical for Spain (32.9% versus 16.1%, and 22.7% versus 15.1%). Foreign-born
living in Spain had the highest level of ESL (38.3%) in EU countries in 2013.
According to IVIE (2013), being a female in Spain reduces the probability of
ESL by 12%, while being a foreigner increases it by 16%.
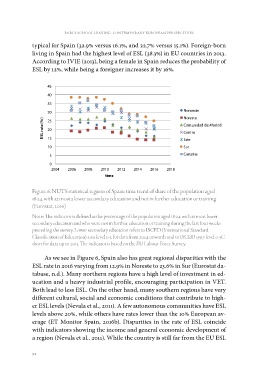
45 Noroeste
40 Noreste
35 Comunidad de Madrid
30 Centro
25 Este
20 Sur
15 Canarias
10
2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018
5 time
0
2004
Figure 6. NUTS statistical regions of Spain: time trend of share of the population aged
18-24 with at most a lower secondary education and not in further education or training
(Eurostat, 2016)
Note: The indicator is defined as the percentage of the population aged 18-24 with at most lower
secondary education and who were not in further education or training during the last four weeks
preceding the survey. Lower secondary education refers to ISCED (International Standard
Classification of Education) 2011 level 0-2 for data from 2014 onwards and to ISCED 1997 level 0-3C
short for data up to 2013. The indicator is based on the EU Labour Force Survey.
As we see in Figure 6, Spain also has great regional disparities with the
ESL rate in 2016 varying from 12.9% in Noreste to 23.6% in Sur (Eurostat da-
tabase, n.d.). Many northern regions have a high level of investment in ed-
ucation and a heavy industrial profile, encouraging participation in VET.
Both lead to less ESL. On the other hand, many southern regions have very
different cultural, social and economic conditions that contribute to high-
er ESL levels (Nevala et al., 2011). A few autonomous communities have ESL
levels above 20%, while others have rates lower than the 10% European av-
erage (ET Monitor Spain, 2016b). Disparities in the rate of ESL coincide
with indicators showing the income and general economic development of
a region (Nevala et al., 2011). While the country is still far from the EU ESL
92
typical for Spain (32.9% versus 16.1%, and 22.7% versus 15.1%). Foreign-born
living in Spain had the highest level of ESL (38.3%) in EU countries in 2013.
According to IVIE (2013), being a female in Spain reduces the probability of
ESL by 12%, while being a foreigner increases it by 16%.
45 Noroeste
40 Noreste
35 Comunidad de Madrid
30 Centro
25 Este
20 Sur
15 Canarias
10
2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018
5 time
0
2004
Figure 6. NUTS statistical regions of Spain: time trend of share of the population aged
18-24 with at most a lower secondary education and not in further education or training
(Eurostat, 2016)
Note: The indicator is defined as the percentage of the population aged 18-24 with at most lower
secondary education and who were not in further education or training during the last four weeks
preceding the survey. Lower secondary education refers to ISCED (International Standard
Classification of Education) 2011 level 0-2 for data from 2014 onwards and to ISCED 1997 level 0-3C
short for data up to 2013. The indicator is based on the EU Labour Force Survey.
As we see in Figure 6, Spain also has great regional disparities with the
ESL rate in 2016 varying from 12.9% in Noreste to 23.6% in Sur (Eurostat da-
tabase, n.d.). Many northern regions have a high level of investment in ed-
ucation and a heavy industrial profile, encouraging participation in VET.
Both lead to less ESL. On the other hand, many southern regions have very
different cultural, social and economic conditions that contribute to high-
er ESL levels (Nevala et al., 2011). A few autonomous communities have ESL
levels above 20%, while others have rates lower than the 10% European av-
erage (ET Monitor Spain, 2016b). Disparities in the rate of ESL coincide
with indicators showing the income and general economic development of
a region (Nevala et al., 2011). While the country is still far from the EU ESL
92