Page 189 - Štremfel, Urška, ed., 2016. Student (Under)achievement: Perspectives, Approaches, Challenges. Ljubljana: Pedagoški inštitut. Digital Library, Documenta 11.
P. 189
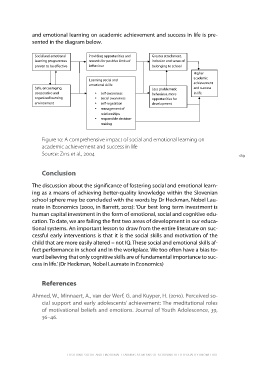
emotional learning on academic achievement and success in life is pre-
sented in the diagram below.
Social and emotional Providing opportunities and Greater attachment, Higher
learning programmes rewards for positive kinds of inclusion and sense of academic
proven to be e ective behaviour belonging to school achievement
and success
Safe, encouraging, Learning social and Less problematic
cooperative and emotional skills: behaviour, more in life
organized learning opportunities for
environment • self-awareness development
• social awareness
• self-regulation
• management of
relationships
• responsible decision-
making
Figure 10: A comprehensive impact of social and emotional learning on 189
academic achievement and success in life
Source: Zins et al., 2004
Conclusion
The discussion about the significance of fostering social and emotional learn-
ing as a means of achieving better-quality knowledge within the Slovenian
school sphere may be concluded with the words by Dr Heckman, Nobel Lau-
reate in Economics (2000, in Barrett, 2012): ‘Our best long term investment is
human capital investment in the form of emotional, social and cognitive edu-
cation. To date, we are failing the first two areas of development in our educa-
tional systems. An important lesson to draw from the entire literature on suc-
cessful early interventions is that it is the social skills and motivation of the
child that are more easily altered – not IQ. These social and emotional skills af-
fect performance in school and in the workplace. We too often have a bias to-
ward believing that only cognitive skills are of fundamental importance to suc-
cess in life.’ (Dr Heckman, Nobel Laureate in Economics)
References
Ahmed, W., Minnaert, A., van der Werf, G. and Kuyper, H. (2010). Perceived so-
cial support and early adolescents’ achievement: The meditational roles
of motivational beliefs and emotions. Journal of Youth Adolescence, 39,
36–46.
fostering social and emotional learning as means of achieving better-quality knowledge
sented in the diagram below.
Social and emotional Providing opportunities and Greater attachment, Higher
learning programmes rewards for positive kinds of inclusion and sense of academic
proven to be e ective behaviour belonging to school achievement
and success
Safe, encouraging, Learning social and Less problematic
cooperative and emotional skills: behaviour, more in life
organized learning opportunities for
environment • self-awareness development
• social awareness
• self-regulation
• management of
relationships
• responsible decision-
making
Figure 10: A comprehensive impact of social and emotional learning on 189
academic achievement and success in life
Source: Zins et al., 2004
Conclusion
The discussion about the significance of fostering social and emotional learn-
ing as a means of achieving better-quality knowledge within the Slovenian
school sphere may be concluded with the words by Dr Heckman, Nobel Lau-
reate in Economics (2000, in Barrett, 2012): ‘Our best long term investment is
human capital investment in the form of emotional, social and cognitive edu-
cation. To date, we are failing the first two areas of development in our educa-
tional systems. An important lesson to draw from the entire literature on suc-
cessful early interventions is that it is the social skills and motivation of the
child that are more easily altered – not IQ. These social and emotional skills af-
fect performance in school and in the workplace. We too often have a bias to-
ward believing that only cognitive skills are of fundamental importance to suc-
cess in life.’ (Dr Heckman, Nobel Laureate in Economics)
References
Ahmed, W., Minnaert, A., van der Werf, G. and Kuyper, H. (2010). Perceived so-
cial support and early adolescents’ achievement: The meditational roles
of motivational beliefs and emotions. Journal of Youth Adolescence, 39,
36–46.
fostering social and emotional learning as means of achieving better-quality knowledge